According to several reports there will be 50 billion connected devices by 2020. The Internet of Things (IoT) is spreading its divisions across diligences, organization, utilities, homes, and almost everywhere. IoT is helping in the next Industrial Revolution and will enable new form of analytics to analyze a massive cloud of dynamic, ever changing information and offer information that can be used for operative and analytical purposes. However, its first and greatest impact is expected to be in the industrial sector, where organised change is more feasible than in sectors where the public are involved.
According to Hrishikesh Kamat, CEO, Shalaka Technologies, “The IoT is regarded as a disruptive technology and a game changer. IoT is a network of physical real world objects that can sense information using different sensors, send the information using internet connectivity and perform actions as required. This helps dumb objects capable of understanding various parameters and reacting to stimuli.”
What is industrial IoT?
Industrial IoT is termed as IIoT which refers to IoT technologies in manufacturing. IIoT incorporates machine-to-machine communication, machine learning, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data technology, harnessing the sensor data and using them for preventive and predictive maintenances. The driving philosophy behind the IIoT is that smart machines are better than humans at accuracy, consistently capturing and communicating data.
“IIoT is the next generation of digital technology centered on smartly optimizing the industrial processes so as to enable the manufacturers to make the most of the industrial internet revolution,” says Sameer Gandhi, MD, Omron Automation, India.
Process cycle of IIOT: Collecting data from sensors (things) – decoding this data strategically using big data analytics to turn them into actionable information – presenting this actionable information to the right person at the right time – delivering efficiency by taking corrective action.
IIoT is actually an extension of factory automation and connectivity that has been a part of the manufacturing environment for decades. It’s high level of automation backed by huge data. These data are then further analyzed to make machines intelligent that can take decisions on their own.
“IIoT is a system that incorporates complex machines with high-end software programs and sensors for collecting the real time data and analyzing it to increase productivity and reduce operational time and costs,” avers Hrishikesh.
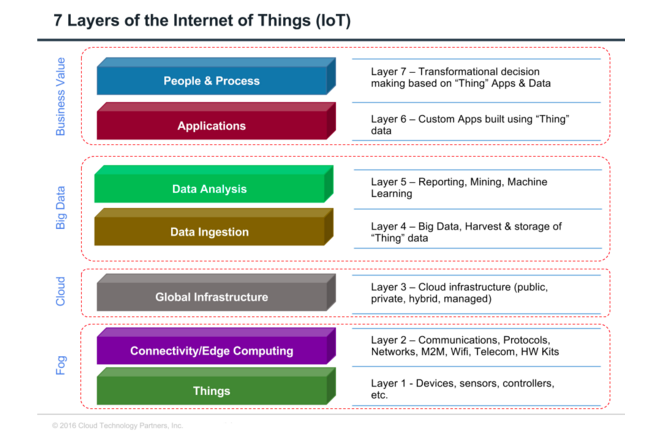
Building blocks of Industrial IoT
The building blocks of Industrial IoT constitute of Sensing Node (Sensor), Processing Node (MCU), Connectivity Node (Wired/Wireless), Remote Embedded Processing Node and Cloud Computing and Digital Signal Processors. This building block will also have correspondent at each controller unit, software for each block, security in terms of integrity, confidentiality & reliability of the data being communicated between the blocks. Built-in hardware security at each node will be an essential requirement.
Says Sameer Gandhi, “This technology is an intricate and fascinating network of products, systems, platforms and applications communicating and sharing intelligence with each other & the manufacturing environment including the people. So it is basically not only making the machines intelligent but also making them communicate with each other and with their operators. This, over a period of time, leads to superior levels of optimization further leading to real time waste management, economies of scale by bringing down the operating cost and, thus, production of better output which benefits not only the manufacturers but the end users too.”
Applications of Industrial IoT
IIoT has application in every industry in all departments like maintenance, production, design, inventory management, operation and logistics, among others. IIoT enabled device can be used for many industrial applications like monitoring electricity consumption, viscosity of material, vehicle tracking, machine health monitoring, detection of harmful gases, raising alert, detection of sulphur to prevent corrosion, temperature, pressure & humidity monitoring, and many others. These are just tiny little hand-picked applications but IIoT has acceptability in almost all the industrial setup.

“The technology provides the possibility of achieving extraordinary levels of productivity while constantly assessing risks and relationships. At the core of the technology, currently, are varied smart sensors and PLCs that can connect to the MES/ERP layer facilitating access to real-time information exchange,” adds Sameer Gandhi.
Agrees Hrishikesh, “IoT helps to bring in traceability in the Manufacturing platform. Traceability is the ability to document the history, location or application of the item. Like for example, operator of the CNC, part machined, duration, time and other machine related information during time of action.”
Benefits of IIoT
Thought leaders around the world say the most valued companies will be those that blend digital capabilities and industrial assets.
“Introducing IoT flavour in CNC helps increase operational efficiency and increase throughput. This would eventually result in lesser manufacturing cost and better financial margins. IoT helps bring in intangible advantages like predicting machine breakdown and preventing/reducing downtime by taking proper measures. This helps to ensure that machines run at best efficiency and provide best throughput,” says Hrishikesh.
IIoT can help in:
- Predictive maintenance efficiencies: Machine break down is the biggest nightmare for any plant manager, this directly impacts the overall production cycle of the company and output. Placing sensors in equipment or machines and pairing them with software allows companies to predict when equipment will fail, and it gives them the opportunity to fix problems well before the breakdown.
- Innovative ways to track and analyze equipment: While predictive maintenance is a great way to use sensors for the IIoT, other companies are using them for real-time data tracking. Michelin sells some of its tires with embedded sensors to track fuel consumption, tire pressure, temperature, speed, and location in fleet trucks. That data is then sent to a cloud service, where company analysts look at the data and recommend to truck fleet managers how they can save fuel.
- Increased revenues: Even though it’s very early to come up with some numbers about the increase in revenue or decrease in expenditure on factory maintenance or machine breakdown, the benefits are clearly visible as IIoT helps in increasing efficiency, saving money in maintenance, realizing full potential of the machine and enhance productivity. This clearly reflects on the overall revenue of the company. According to Accenture, the value from IIoT technologies and services could bring in up to $15 trillion in global GDP by 2030.

Just to give an example Sameer adds, “Imagine an automotive assembly line, which would typically have a few thousand sensors. Now if any of these sensors fail, the entire line could stop working, which will require manual identification and repair/ replacement, leading to non-productive time. With IIoT, Omron is enabling to connect the sensor in a way, wherein we’re not only getting information from the sensor but also about the sensor. So we can now look into ambient conditions affecting the sensors and other deeper aspects, allowing us to predict the failure of a sensor, before it actually happens.”
India’s take on IIoT
The Indian Government’s plan to develop 100 smart cities in the country, for which Rs. 7,060 crores have been allocated in the current budget could lead to a massive and quick expansion of IoT in the country. Also, the launch of the Digital India Program of the Government, which aims at ‘transforming India into digital empowered society and knowledge economy’ will provide the required impetus for development of the IoT industry in the country. The various initiatives proposed to be taken under the Smart City concept and the Digital India Program to setup Digital Infrastructure in the country would provide a needed boost to the IoT industry. IoT will be critical in making these cities smarter.
Apart from this, programs like Make in India have boosted the investment sentiment in the country. Many global giants are setting up manufacturing facilities in India and Indian conglomerates along with SMEs are looking for more and more automation. This trend will certainly drive the future of the Indian IIoT market.
Department of Electronics and Information Technology, (DeiTY) has come out with a draft IOT Policy document which focuses on following objectives:
- To create an IoT industry in India of USD 15billion by 2020. It has been assumed that India would have a share of 5-6% of global IoT industry.
- To undertake capacity development (Human & Technology) for IoT specific skill-sets for domestic and international markets.
- To undertake research & development for all the assisting technologies.
- To develop IoT products specific to Indian needs in all possible domains.
The Policy framework of the IoT Policy has been proposed to be implemented via a multi-pillar approach. The approach comprises of five vertical pillars (Demonstration Centres, Capacity Building & Incubation, R&D and Innovation, Incentives and Engagements, Human Resource Development) and 2 horizontal supports (Standards & Governance structure).
Talking about the current state of Indian IoT industry, Hrishikesh says, “India has huge opportunities for IoT solution providers like us and we are very excited to be part of this growing IoT ecosystem in the country. Even though this technology is in very nascent stage in India where many companies are yet to adopt basic level of automation, we believe in the next 5 years there would be huge demand for embedded system, connected devices, cloud platform, data analytics services, high-end sensors, among others. We welcome the move of Indian government to further boost the adoption and development of IoT system in India.”
Future Ahead
Experts believe that the Industrial IoT market is going to be bigger than consumer IoT. According to General Electric, by 2020, revenues generated from the IIoT market will be about $225 billion. In comparison, GE forecasts the consumer IoT will only generate about $170 billion by that time. This clearly shows the opportunities in IIoT segment.
With companies investing a lot of money in IIoT and more and more devices are to be connected with internet in the coming future, India is not going to be left behind. Indian companies, be it small, medium or large OEMs, have realized the potential of IoT and ready to be part of growth story.
“Indian companies are looking forward with great enthusiasm and are ready to incorporate Research and Development activities into their organization. Many Indian OEM’s are looking towards Smarter Factories that are inclined towards higher efficiency and lesser downtimes. Many Indian Companies are looking forward towards incorporating concepts like IIoT, M2M communication and centralised data analysis and control,” concludes Hrishikesh


